PHOTO
(The author is a Reuters Breakingviews columnist. The opinions expressed are her own.)
MUMBAI - India has slender room to act if economic activity follows its medical infrastructure into a virus-induced state of collapse. So far there’s a wide gap between the two measures of health. Optimists hope antibodies and vaccines will cause the Covid-19 contagion to burn out quickly. The government will have a hard time softening the financial pain if it doesn’t.
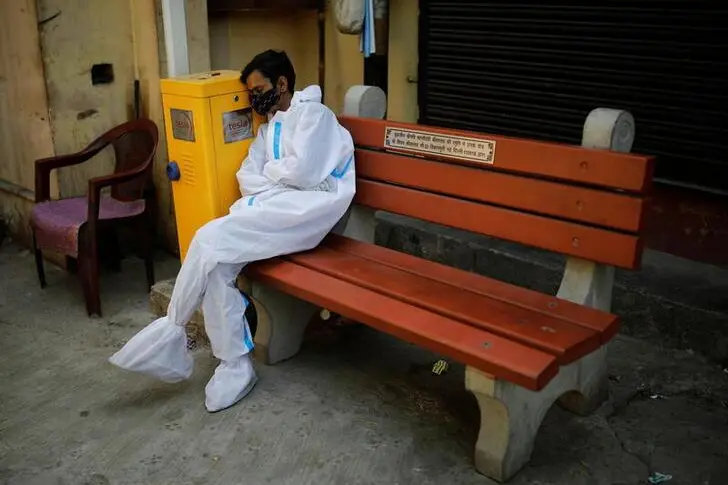
The second wave is proving more virulent than the first; India recorded the world’s highest daily tally of infections at 314,835 on Thursday. Hospitals are running out of oxygen; even fancy private healthcare facilities in Mumbai and New Delhi can’t keep pace. People are turning to makeshift facilities for mass cremations.
Productivity has fallen, but the descent is less precipitous than might be expected. Limits on movement are more localised than in last year’s national lockdown, which led to a stunning 23.9% contraction in GDP in the June quarter from a year earlier. Many factories are still running, albeit churning out fewer goods, and construction work continues. Restrictions have also come into effect later along the crisis curve.
The equity market has corrected slightly. But the crisis could force sharper lockdowns. Foreign investors look jittery, turning into net sellers of Indian debt and equity in April, and the rupee has depreciated sharply.
One whispered hope is that the spike in infections will be followed by a rapid fall as immunity increases and the vaccine rollout gains momentum. Neelkanth Mishra and team at Credit Suisse estimate some 40% of the population might have antibodies by the end of April. A foundation led by Bain Capital India Managing Director Amit Chandra projects a higher result for Mumbai, tipping it closer to 65% where infections might fall off. Yet epidemiologists worried about virus variants are much less confident.
The country is home to the Serum Institute, the world’s top vaccine maker, and politicians are opening the doors to imported jabs, but supply will be tight. Calls are growing for income support; ordinary folks have burnt through savings, in part because the government was frugal with handouts in the first wave. Even so, India has exhausted most of its monetary and fiscal space, one central bank director bleakly noted in meeting minutes released on Thursday. That leaves unorthodox alternatives if hope is misplaced.
CONTEXT NEWS
- India recorded the world's highest daily tally of 314,835 coronavirus infections on April 22.
(The author is a Reuters Breakingviews columnist. The opinions expressed are her own.)
(SIGN UP FOR BREAKINGVIEWS EMAIL ALERTS http://bit.ly/BVsubscribe | Editing by Pete Sweeney and Katrina Hamlin) ((una.galani@thomsonreuters.com; Reuters Messaging: una.galani.thomsonreuters.com@reuters.net))